- home
- project
- Forschung
- research
- investigación
- исследование
- recherche
- BWL
- Betrieb
- Finanzen
- Noteninflation
- Schummelkultur
- Akademisierung
- Männerrechte
- Politik
4.7. Investment and general items
4.7.1. Investment (36)
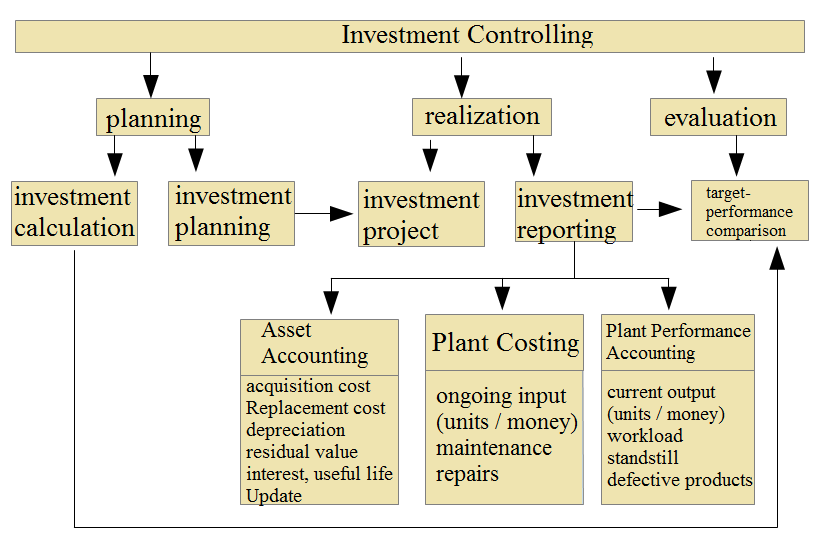
The procurement of repeat factors is not directly incorporated in the value added. Because about 80% of the future costs are determined by the investment, a careful decision and selection with
the help of the investment calculation is very important. An investment controlling to create a better database for optimizing investment decisions is recommended. With replacement investments
and expansion investments, the future, in which an investment should have an impact, can be derived relatively reliably from the past. In rationalization investments, where new technologies are
often to be used, this is less the case. Nevertheless, you will not want to give up experience in these decision situations. Even in accounting 2.0, the asset reporting serves as a database for
this purpose.
From the machine master data the age and the condition of the machines can be read. (Arrow 50) These data provide an assessment of the need for expansion or replacement investment. In this
function, investment controlling should also collect data on the condition of equipment, probable replacement costs, and on their ongoing costs and services. Procurement market research should
also gather up-to-date information for capital goods. (Arrow 51) When deciding on an investment, the supply chain (request => offer => order) is triggered. (Arrow 52) The chain would be
completed with the delivery of the capital goods and their start-up. (Arrow 53)
Fig. 29: Investment controlling
(Source: https://mueller-consulting.jimdo.com/research/building-site/technology/)
In Accounting 3.0, asset accounting can thus be expanded into a complex investment controlling that would not be feasible with the 1494 technology. In Fig. 23 on page 96 investment activity has
been described as having the color of the rectangle as an organizational task.
4.7.2. Depreciation (37)
The ongoing wear and tear must be recorded as depreciation. On the one hand, a periodization of the acquisition costs should take place for the accounting. On the other hand, substance
conservation is to be organized via the sales process, which is why the current replacement costs are a more appropriate basis here. The estimation of the remaining useful life may also change in
the last third of the useful life estimated at acquisition due to new findings. Depreciation can also be based on investment controlling.
Capital goods wear off through use, which must be recorded through depreciation. (Arrow 54) A depreciation plan simulates the depreciation for the future useful life. Tax depreciation may deviate
from your own assessment. After about two thirds of the scheduled useful life, a reassessment of the remaining useful life makes sense. Depreciation is included in the cost of goods sold. (Arrow
55)
In Fig. 23 on page 96 depreciation has been described as having the color of the rectangle as an accounting task. In Fig. 24 on page 97 these and the previous task were assigned to the module
"Investment and Financing" with the letter "J". been assigned. Here, investment controlling (see Fig. 29 on page 135) is extended to include an overview of longer-term financing, which is also
"worn down" by current repayments.
4.7.3. Overhead costs (38)
The consumption of resources is not limited to the value added stages in the narrower sense. There is also a general area that is not directly related to value creation, but still consumes
resources. The goods required here are also procured in purchasing. These general area costs are called overheads. With the identification as overhead, the relevant cost center is defined. A cost
unit assignment is normally not possible. (Arrow 56) Only in exceptional cases can one imagine that typical overhead costs can be attributed to individual orders. More often, there are typical
direct costs that are not recorded individually for reasons of efficiency. Then one speaks of unreal overhead costs. However, technical progress now allows more frequent data acquisition.
A differentiated outsourcing of the cost centers in the overhead cost area can be useful to allocate the costs to the processes running there. There may be products that more or less use these
processes. If some costs arise for only a limited number of products, then they must also be covered from the sales of these products. If this were not possible, the task of the corresponding
products and the reduction of the costs could make sense. Even outside such extreme situations, austerity measures in overheads are popular measures to improve profitability. Accurate
documentation of costs incurred in the overhead cost centers and the tasks they perform may streamline the discussion and promote continuous improvement in profitability, often more effectively
than spectacular austerity programs that are often only intended to reassure investors.
4.7.4. Personnel Administration (39)
The personnel administration fulfills a task in the creation of value through the coordination of the production factor work. Here payroll is performed and the updating of the processes, e.g. due
to changes in legislation. (Arrow 57) The personnel administration also maintains the employee master data. (Arrow 58) For leave and sick leave, a representation is organized in the personnel
administration, so that the operational functions are not seriously disturbed. The coordination of personnel planning is carried out here, even if the influencing factors come from the value
added process.
The personnel administration function is closely linked to the other functions of the HR department, which are located in the frame of Fig. 23 on page 96. However, human resource management is
linked to the ongoing functions of the value-added process so that it is already mentioned here.



