- home
- project
- Forschung
- research
- investigación
- исследование
- recherche
- BWL
- Betrieb
- Finanzen
- Noteninflation
- Schummelkultur
- Akademisierung
- Männerrechte
- Politik
Accounting without Accountants
The accounting of large companies has changed a lot in the last 30 years. Many manual workflows were rationalized. Even small businesses have had computers for over 20 years, and they can create
technical structures that enable them to generate all the information needed to run a good business without expensive professionals. This task should pay much more attention to business
research.
In a research semester, I had tried and tested processes that enable small businesses to record their business transactions without accounting skills in a spreadsheet. The data would then be
uploaded to a server and machine processed in professional software. A little later, the desired reports would be sent back by e-mail in PDF format. In the meantime, the data in the companies is
very strongly networked and the accounting programs are part of larger enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, which can be described in the following diagram.
Fig .: ERP systems

(Source: own illustration)
The circular arrangement of the various operational functions in the ERP graphic does not indicate any relationships with each other. This would have to be done before the design of an ERP
system. There are a variety of ways to represent the relationships between various operational functions. Here's an example:
Fig .: operational functions

(Source: own illustration)
The value-added process is made possible especially by personnel deployment and the financial sector as a navigation system of corporate governance. These three main functions (highlighted in
yellow) list the most important subfunctions. There are also links marked by the arrows marked with letters. They have the following meaning:
to A:
The vast majority of investment decisions, and most importantly, the value creation process. Here, information from the value creation process is needed for decision-making.
to B:
Investment also requires funding. This is especially true for large-scale investments that are not covered by current revenue from the sales process.
to C:
Information about the scope of these financing options from operating cash flow is therefore required. However, financing does not only affect investments but the entire value creation
process.
to D:
There is a close exchange of information between finance and financing.
to E:
Relations with lenders and shareholders must be maintained with the Investor Relations function, so that further financing options can be opened quickly if required. For this purpose, financial
information is prepared and transmitted.
to F:
Investment decisions are also based on information from the financial sector. Investments made have an importance for corporate planning. Because about 80% of the future costs are determined by
the investment, investment controlling should be recommended for optimizing investment decisions according to the following pattern:

to G:
The finance department needs ongoing information from the value creation process for its planning and control task.
to H:
The personnel deployment is predominantly in the value added process. For personnel recruitment, the personnel requirements must be determined here.
to I:
The value creation process is driven by the sale of the products. Therefore, the relationships with the current and potential customers must be maintained in order to create an optimal
environment for the development of the company.
to J:
The positive environment can also be broader and understood as a social environment. Although this public relations task seeks to maintain the reputation of the company as a whole and independent
of the products, its own target group will remain the starting point.
to K:
The line connecting personnel and finance is largely limited to the exchange of data from payroll accounting and personnel deployment, which are also mainly required for payroll and order
billing.
From the value chain, the current processes can be structured as follows:
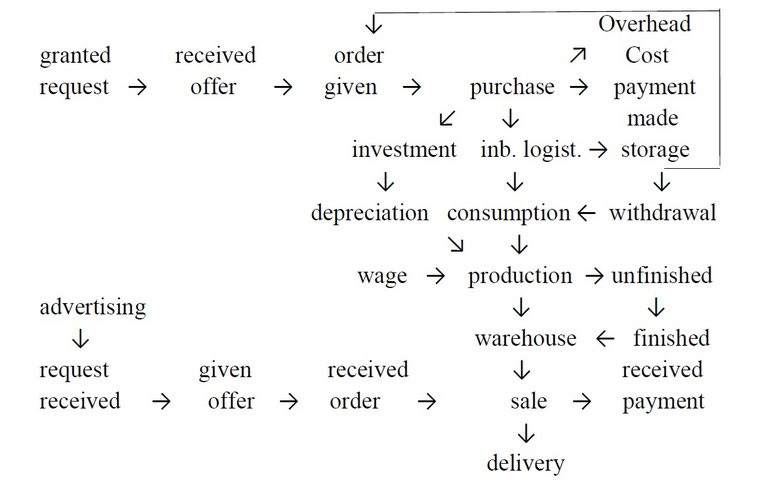
E x p l a n a t i o n :
ERP system
Enterprise resource planning is about the holistic capture, mapping and control of value creation processes. Data will be gathered for the future, but based on past data. An ERP software
accompanies all stages of the graphic above with a data acquisition. It is often necessary to collect data on quantity and monetary units. The approach "Quantity × Price = Amount", but also
"Amount: Quantity = Ø Price" or "Amount: Price Index = Amount" can be used. Accounting and controlling also access the data.
granted request
It is noted at which suppliers one has asked for which products. If you have refusals or no answers, you do not need to ask again.
received offer
The collection of unsolicited offers and responses to inquiries can also be a guide to future purchases. One knows the sources of supply and the price level.
Order given
Orders are placed based on current or past offers. If delivered later, you should check compliance with the appointment. For this, a file with assigned jobs must exist, which is differentiated
from completed and still running jobs.
purchase
When purchasing, it has to be distinguished whether goods and services have been purchased for consumption in current production, for the general area or whether investment goods for use in
production or in the general area. With the delivery a given order is done. In a less narrow definition, the tasks of inquiry, offer and order are also assigned to purchasing.
For goods that are bought repeatedly, a shopping article no. makes sense, under which the information from inquiry, quotation, order and delivery and later the stocks and consumption quantities
can be recorded and evaluated.
inbound logistics
The purchases must go to the place of consumption. This can be done by the supplier delivering directly to the place of consumption or by organizing this transport in-house. It is also possible
that the goods must be collected from the seller. For several different consumption types, intermediate storage in a material store is common. In inbound logistics, it must be known when and
which transport must be carried out and which goods are to be stored where.
material storage
The storage is associated with administrative costs for entry and removal and for the ongoing operation of the warehouse. In this task, up-to-date data on the size of the stocks and on the
turnover frequency must be generated.
withdrawal
When removing material from the warehouse, there is not only the amount of data collected according to the pattern "what? Where? for what? perform. "What?" Is the article no. covered. This
involves updating the current inventory and controlling the optimal order quantities and times. "Where?" Specifies the area of responsibility in which the material is used and "for what?" The
manufactured product or the completed order.
consumption
Consumption can be from a direct delivery or a withdrawal from stock. Services are always bought directly. Withdrawals can be recorded concretely or calculated retrogradely from the output. The
result of the production over a period of time may be finished or unfinished products.
production
In production, the combination of the production factors capital and labor takes place. Capital distinguishes between potential factors that are slow to wear off and repetitive factors that are
constantly being replaced.
unfinished
Work in progress is already consuming resources. They are therefore output of the current and input of the next period. The measurement and evaluation of unfinished products is fraught with
difficulties, because not only their number but also the degree of completion should be determined. Here is to look for suitable simplifications.
finished
The finished products are available for sale. A central task is to compare the costs of manufacturing and distributing the products as well as the proportionate administrative costs to the sales
and thus to assess the different profitability of the different products.
Product warehouse
Finished goods are first stored and kept ready for sale, unless they are individually made for this customer on his order and then shipped immediately. The stock must be constantly kept
up-to-date on stocks and the next additions from ongoing production in order to provide accurate information on customer deliveries requests.
advertising
The success control is difficult with advertising. Nevertheless, in order not to incur useless costs, a goal should be formulated for each advertising measure. Subsequently, the search should be
carried out for the data on which the achievement of the objective could be read. After that, it should be noted to what extent this data has changed.
request received
Requests received from potential customers should be saved and evaluated, even if they did not come to an order. You can tell from them what articles they need and you can try to get orders from
them in the future.
given offer
Offers made are the basis for negotiations with customers. It can be expected that some of the products offered will be taken out later and / or other products added later. There will be several
versions of an offer that should be available later.
received order
The final version of the offer, which is agreed upon with the customer, represents the content of the purchase contract concluded with the customer. If it is fulfilled later, a contract document
or an order confirmation with the contract content and the date of completion should be created here.
sale
A sale in the strict sense is the immediate delivery of the goods to the customer, often against immediate payment. Here is the sales record and issue the customer an invoice or receipt. The
sales function in a broader sense also includes the stages of inquiry, offer, order and delivery.
delivery
This function includes the outbound logistics from the finished parts warehouse to the customer. Good planning means that unnecessary transports and thus costs are to be avoided. It is also
necessary to confirm that the customer has received the goods, e.g. by acknowledging the receipt on a delivery note.
received payment
If the services are not paid immediately, they must be settled with data from the sale. The receipt of payment is to be checked and the customers may be reminded.
payment made
Related goods and services are invoiced by the suppliers if they have not been paid immediately. The due date of the invoices must be recorded and the timely payment must be organized.
wage
The production factor of work is evaluated by wages. The personnel deployment in the value added as well as in the overhead costs area is recorded, evaluated and recorded as the basis for the
payroll accounting. These processes take place in the personnel administration.
Overhead Cost range
The consumption of resources is not limited to the value added stages in the narrower sense. There is also a general area that is not directly related to value creation, but still consumes
resources. The goods required here are also procured in purchasing.
investment
The procurement of repeating factors does not flow directly into value creation. Because about 80% of the future costs are determined by the investment, a careful decision and selection with the
help of the investment calculation is very important. An investment controlling to create a better database for the optimization of investment decisions is recommended.
depreciation
The ongoing wear and tear is to be recorded as depreciation. On the one hand, a periodization of the acquisition costs should take place for the accounting. On the other hand, substance
conservation is to be organized via the sales process, which is why the current replacement costs are a more appropriate basis here. The estimation of the remaining useful life can also change in
the last third of the useful life estimated at acquisition due to new findings. Depreciation may also be based on investment controlling.
The data must be recorded with quantity and monetary units in the following dimensions:
Previous year current ► [extrapolation] ◄ forecast plan
Previous year
The data of the previous year can later be copied from the old files. Whether and to what extent the previous year's data should be inserted from other files in the first year of deployment would
have to be decided on a case-by-case basis.
current
The current data is recorded in the constantly occurring data. The files are empty for the rest of the year.
plan
Once a year goals and realistic expectations are recorded in the format of the current and previous year's data. Thus, all evaluations for the future can be generated, which can be assessed in
terms of plausibility and possibly also be corrected. The objectives and sub-goals set on this basis remain binding during the planned year.
forecast
Based on new insights, the assumptions are updated in a copy of the plan data. Also, measures for a course correction, e.g. Spontaneous austerity measures are incorporated into this data.
extrapolation
From the actual data for the past months and the forecast data for the remainder of the year, an extrapolation is made to the whole year by machine.
But even under these conditions, small businesses can use the full width:
Figure: ERP for small businesses

(own representation)
The individual components of the ERP have to be pulled apart while maintaining the networking. The tasks from the value-adding-chain must be supported by applications that the small business
owner directly applies himself. These are in particular purchase and sale, but also production, inventories and logistics. The corresponding parts of the ERP system have to become autonomous at a
limited extent and a data transfer has to be organized. The task of design or product development is not part of the everyday value-adding-chain, but still an original task of the
entrepreneur.
The areas of Financial Accounting and Management Accounting as well as personnel administration, on the other hand, can be operated with the upload of self-recorded data or data exported from
applications in the value-adding-chain. The use of information technology could use the service of a service provider. The preparation of investment and financing decisions as well as operational
and strategic planning can be supported by a qualified consultant.
It is important that the information flow to the ERP is maintained even with a stronger division of labor with outside support.



